LiveCareer Report: 67% of Workers Believe a Four-Day Workweek Boosts Productivity
A shorter workweek is gaining momentum as a preferred work schedule for many U.S. workers, especially women. The LiveCareer Four-Day Work Week Report surveyed 1,130 individuals and explored how compressing a 40-hour workweek into four days could impact productivity, work-life balance and job satisfaction. Here’s what the data reveals about this workplace trend.
Survey highlights:
- 67% of respondents believe they would be more productive with a four-day workweek, working 10-hour days.
- 76% of women support the shift to a four-day workweek, compared to 57% of men.
- 78% of workers believe AI or automation could enable a four-day workweek, with men being more optimistic (86%) than women (71%), revealing a strong reliance on technology to reshape work structures.
- Men are significantly more concerned than women about the schedule’s impact on reduced collaboration time (48% vs. 28%).
- Women place greater emphasis on fewer meetings and remote work options as productivity boosters (50% and 39%, compared to 39% and 22% for men).
A Four-Day Workweek is the Preferred Work Schedule
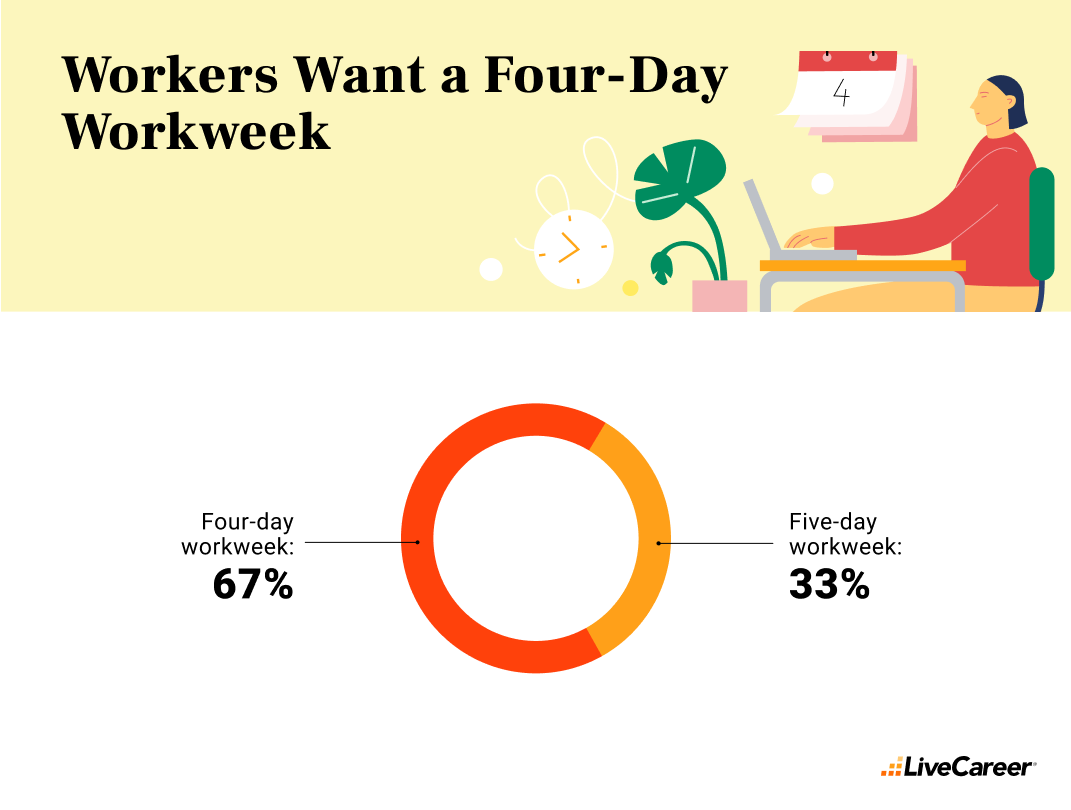
The report found that workers overwhelmingly favor a four-day workweek. Sixty-seven percent of those surveyed feel they would be most productive working four 10-hour shifts compared to a third who say they favor a five-day, 40-hour-a-week schedule.
What it means: This indicates a strong preference for a more condensed work schedule, reflecting workers’ desire for flexibility without compromising productivity.
Gendered Differences in Preferences
A four-day workweek has broad support among women who value better work-life balance and flexibility.
- 76% of women prefer a four-day workweek, compared to 57% of men.
- Men are more likely to prefer the traditional five-day schedule (43%) than women (24%).
What it means: Women’s preference for a shorter workweek highlights the importance of workplace policies prioritizing balance and flexibility, while men’s higher interest in traditional schedules suggests varying needs across genders.
Workers See Potential in a Four-Day Workweek
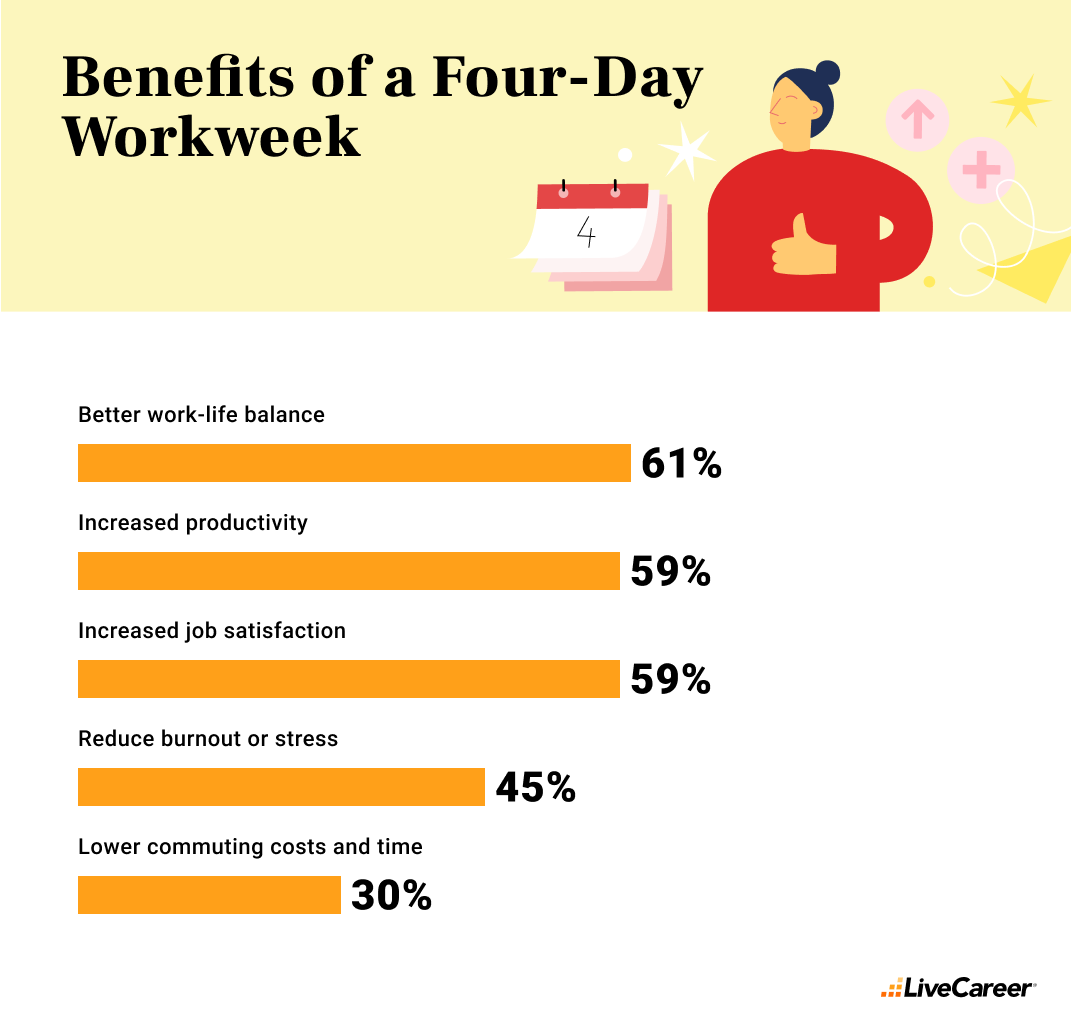
Part of the appeal of a four-day, 40-hour workweek is the perceived benefits of this type of schedule. Of those surveyed, the top benefits include:
- Better work-life balance (61%)
- Increased productivity (59%)
- Increased job satisfaction (59%)
Women, in particular, are interested in a four-day schedule’s ability to help them prioritize work-life balance (69%) and lower commuting costs (40%), compared to 52% and 21% of men, respectively.
What it means: The potential advantages of a four-day schedule align closely with worker’s aspirations for improved well-being and efficiency.
Workers Fear Productivity Problems
When asked what they predict would be the biggest challenges to staying productive in a four-day workweek, workers did cite several trade-offs:
- 63% say that a four-day workweek would result in longer workdays, leading to fatigue.
- 59% believe a condensed schedule can potentially increase their workload or expectations.
- Men are more concerned about a four-day workweek creating an increased workload (69%) than women (58%).
- Men also worry that an abbreviated workweek would mean less time for collaboration (48%) compared to women (28%).
What it means: While a four-day workweek is appealing, concerns about fatigue and workload indicate that organizations must carefully plan its implementation to mitigate potential drawbacks.
Strategies for Boosting Productivity in a Four-Day Workweek
Surveyed workers shared the top tools and strategies they believe will support productivity in a four-day week:
- Better time management or productivity tools (54%)
- Setting clearer priorities and goals (51%)
- Shifting the focus onto professional outcomes over the number of hours worked (45%)
Women put greater emphasis on fewer meetings and remote work options as productivity boosters (50% and 39%, compared to 39% and 22% for men), shedding light on how different groups prioritize work practices to improve efficiency.
What it means: Tailoring productivity strategies to workers’ specific needs can enhance the effectiveness of a four-day workweek.
Optimism About AI and Automation
Additionally, most of those polled say that they believe AI and automation will significantly improve the productivity of a four-day workweek:
- 78% believe AI or automation could enable a four-day workweek.
- Men are more optimistic (86%) about AI’s role in a shortened workweek than women (71%).
What it means: The integration of technology is seen as a key enabler of shorter workweeks, highlighting the importance of investing in tools that support efficiency.
The findings from the LiveCareer 4-Day Work Week Report highlight a growing shift in workers’ priorities, with many envisioning a future where productivity and well-being are equally valued. While a four-day workweek offers undeniable appeal — particularly among women — it also presents challenges that need addressing, such as managing longer hours and potential workload increases. Ultimately, workers see promise in leveraging technology and adopting strategies that align with their diverse needs, highlighting a collective desire for a more balanced and flexible approach to work.
Methodology
The findings were obtained by surveying 1,130 U.S. workers on Nov. 27, 2024, about how they feel a four-day workweek might impact their workplace productivity. They answered different types of questions, including yes/no, open-ended, scale-based questions where respondents indicated their level of agreement with statements, and multiple-choice where they could select from a list of provided options.
About LiveCareer
LiveCareer’s online Resume Builder is designed to empower its users to get better jobs and improve their job search. A one-stop shop among AI resume builder tools, LiveCareer features cutting-edge resume templates, a powerful cover letter builder, and extensive free career resources to support job candidates in reaching their professional goals. Trusted by over 10 million users around the world, LiveCareer has been publishing expert advice from Certified Professional Resume Writers since 2005. LiveCareer’s career tips have been featured in renowned media outlets, including Bloomberg, Forbes, and Newsweek. Stay connected with LiveCareer’s latest updates to improve your job search on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and X.